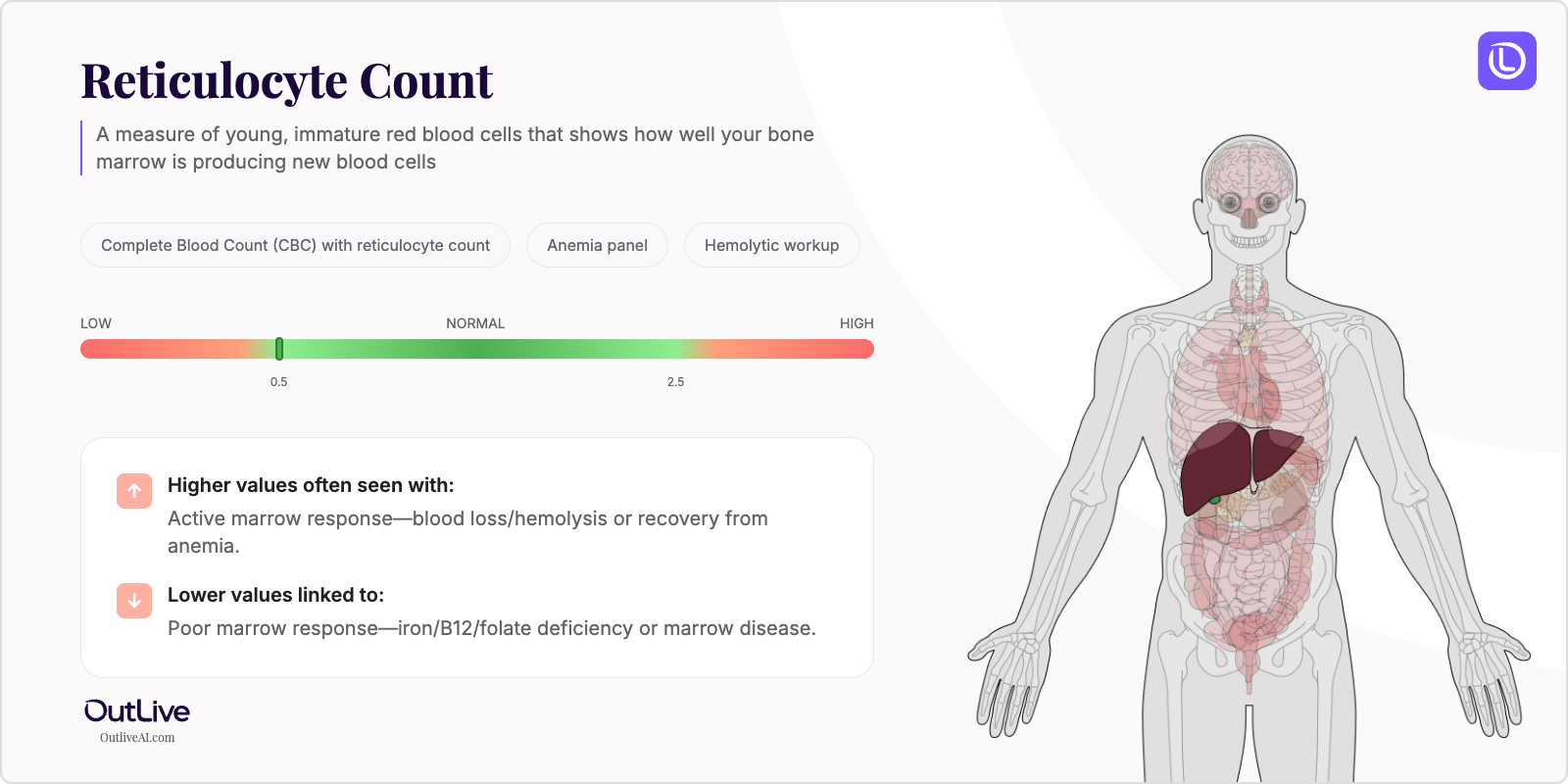
📋 At a Glance
- What it is: A measure of young, immature red blood cells that shows how well your bone marrow is producing new blood cells
- Found in tests: Complete Blood Count (CBC) with reticulocyte count, Anemia panel, Hemolytic workup
- Normal range: 0.5-2.5% of total red blood cells (varies slightly by age and lab)
If you're looking at your lab results and wondering what reticulocyte means, you're in the right place. Think of reticulocytes as the "teenagers" of your red blood cells – they're not quite mature yet, but they're almost ready to do their job of carrying oxygen throughout your body. Let's break down what your numbers mean in plain English.
Why Is Reticulocyte Count Tested?
Your doctor orders a reticulocyte count to understand how well your bone marrow – the blood cell factory in your bones – is working. This test is particularly valuable when you're experiencing symptoms like unexplained fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath that might signal anemia or other blood disorders.
The reticulocyte count becomes especially important when your regular blood count shows abnormal results. If your red blood cell count or hemoglobin is low, the reticulocyte count helps your doctor understand whether your body is trying to fix the problem by making more red blood cells, or if the production line itself has slowed down.
This test also plays a crucial role in monitoring how well you're responding to treatment. If you're taking iron supplements for anemia or receiving other treatments that affect blood production, your reticulocyte count shows whether your bone marrow is responding appropriately.
What Does Reticulocyte Count Do in Your Body?
Reticulocytes are essentially red blood cells in their final stage of development – like butterflies about to emerge from their cocoons. They spend about 1-2 days in your bloodstream finishing their maturation before becoming fully functional red blood cells that will live for about 120 days.
Your bone marrow constantly produces these young cells to replace old red blood cells that your body naturally removes. In a healthy person, this production line runs smoothly, maintaining a steady supply of oxygen-carrying cells. The reticulocyte count gives us a window into this production process – it's like checking the assembly line speed at a factory.
When your body needs more red blood cells – perhaps due to blood loss or increased oxygen demands – your bone marrow can increase reticulocyte production up to 6-8 times the normal rate. This remarkable ability to adjust production is what helps your body maintain the right balance of red blood cells under different conditions.
What Do My Reticulocyte Results Mean?
Normal Reticulocyte Ranges
| Population | Normal Range | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Adult Male | 0.5-2.5% (23-90 × 10⁹/L) | 0.8-2.0% |
| Adult Female | 0.5-2.5% (23-90 × 10⁹/L) | 0.8-2.0% |
| Children (2-6 years) | 0.5-1.5% | 0.7-1.3% |
| Newborns | 2.5-6.5% | 3.0-5.0% |
| Pregnancy (3rd trimester) | 1.0-3.0% | 1.5-2.5% |
Note: Reference ranges may vary slightly between laboratories. Always compare your results to the range provided on your specific lab report.
What Does High Reticulocyte Mean?
Common Causes:
- Recent blood loss (surgery, injury, heavy menstrual periods, or internal bleeding)
- Hemolytic anemia (your body destroys red blood cells too quickly)
- Response to anemia treatment (iron, B12, or folate supplementation showing it's working)
- Recovery from bone marrow suppression (after chemotherapy or severe illness)
- Living at high altitude (your body makes more red blood cells for oxygen)
- Certain medications (erythropoietin, corticosteroids)
- Sickle cell disease or thalassemia (genetic blood disorders)
Possible Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Mild jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Dark urine (tea-colored)
- Enlarged spleen
- Fatigue despite treatment
When to Be Concerned: If your reticulocyte count is extremely high (above 5-6%) and you're experiencing severe fatigue, chest pain, severe shortness of breath, or signs of jaundice, contact your healthcare provider promptly. These could indicate active hemolysis (red blood cell destruction) that needs immediate attention.
What Does Low Reticulocyte Mean?
Common Causes:
- Iron deficiency anemia (not enough building blocks for red blood cells)
- Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency (essential nutrients missing)
- Bone marrow disorders (aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome)
- Chronic kidney disease (kidneys not producing enough erythropoietin hormone)
- Chronic inflammatory conditions (rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease)
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy effects
- Alcoholism (affects bone marrow function)
Possible Symptoms:
- Profound fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin, nail beds, or gums
- Shortness of breath with minimal activity
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Cold hands and feet
- Frequent infections
When to Be Concerned: A very low reticulocyte count with severe anemia symptoms requires prompt medical evaluation. If you're experiencing chest pain, severe shortness of breath, confusion, or fainting, seek immediate medical care as these could indicate your body isn't getting enough oxygen.
What Can Affect My Reticulocyte Levels?
Factors That May Increase Levels:
- Medications: Erythropoietin, corticosteroids, antimalarial drugs
- Lifestyle: Recent blood donation, intense athletic training, moving to high altitude
- Conditions: Pregnancy (especially third trimester), recovery from illness
- Supplements: Recent start of iron, B12, or folate supplements
Factors That May Decrease Levels:
- Medications: Chemotherapy drugs, chloramphenicol, azathioprine
- Lifestyle: Chronic alcohol use, poor nutrition, extreme dieting
- Conditions: Chronic infections, autoimmune disorders, liver disease
- Time of Day: Minor variations (usually tested in morning for consistency)
How Is Reticulocyte Count Related to Other Tests?
Your reticulocyte count works like a puzzle piece that helps complete the picture of your blood health. It's rarely interpreted alone but rather alongside other blood tests to understand what's happening in your body.
Often tested alongside: Hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cell count, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), iron studies, vitamin B12, folate Part of: Complete Blood Count (CBC), Anemia workup panel Ratio calculations: Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI), Corrected Reticulocyte Count Follow-up tests: Iron studies, hemoglobin electrophoresis, bone marrow biopsy (if indicated)
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should reticulocyte be tested? For most people, reticulocyte testing is done when investigating anemia or monitoring treatment response. If you're being treated for anemia, your doctor might check it weekly initially, then monthly as you improve. For chronic conditions, testing every 3-6 months is typical.
Can I improve my reticulocyte levels naturally? If your levels are low due to nutritional deficiencies, eating iron-rich foods (lean meats, leafy greens), B12 sources (fish, dairy), and folate-rich foods (legumes, fortified grains) can help. However, always work with your doctor to identify and treat the underlying cause.
Should I fast before a reticulocyte test? No fasting is required for a reticulocyte count. You can eat and drink normally before the test.
How quickly can reticulocyte levels change? Reticulocyte levels can begin changing within 2-3 days of starting treatment for deficiencies. Peak response usually occurs within 7-10 days. If your bone marrow is healthy, you might see improvement in your reticulocyte count before your hemoglobin levels improve.
Next Steps After Your Reticulocyte Test
Questions to Ask Your Doctor:
- What do my reticulocyte results mean for my overall health?
- Are my levels related to my symptoms?
- Do I need additional testing?
- Should we monitor this over time?
- Are there lifestyle changes that could help?
Download our Reticulocyte Count Doctor Questions Checklist
🔬 Ready to Track Your Reticulocyte Count Over Time?
Understanding a single reticulocyte result is just the beginning. Our free Lab Analyzer tool helps you:
- Track how your Reticulocyte changes over time
- See how it relates to your other lab values
- Identify patterns your doctor might miss
- Get personalized insights based on your trends
[Upload Your Lab Report for Free Analysis →]